|
|
|
Sponsored Link •
|
|
Advertisement
|
The weaker forms of reachability involve an entity that was first introduced in version 1.2: the reference object. A reference object encapsulates a reference to some other object, called the referent. All reference objects are instances of subclasses of the abstract java.lang.ref.Reference class. The family of Reference classes, which is shown in Figure 9-3, includes three direct subclasses: SoftReference, WeakReference, and PhantomReference. A SoftReference object encapsulates a "soft reference" to a referent object; A WeakReference object encapsulates a "weak reference" to a referent object; And a PhantomReference, unsurprisingly, encapsulates a "phantom reference" to a referent object. The fundamental difference between a strong reference and its three progressively weaker cousins -- soft, weak, and phantom references -- is that whereas a strong reference prevents its referent from being garbage collected, soft, weak, and phantom references do not.
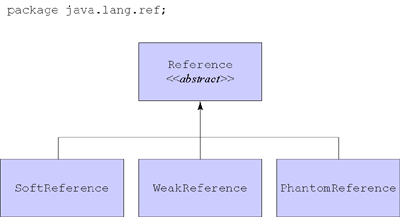
Reference family.
To create a soft, weak, or phantom reference, you simply pass a strong reference to the constructor of the appropriate type of reference object. For example, to create a soft reference to a particular Cow object, you pass to the constructor of a new SoftReference object a strong reference that refers to the Cow object. By maintaining a strong reference to the SoftReference object, you maintain a soft reference to the Cow object.
Figure 9-4 shows such a SoftReference object, which encapsulates a soft reference to a Cow object. The SoftReference object is strongly referenced from a local variable, which, like all local variables, serves as a root node for the garbage collector. As mentioned previously, references contained in garbage collection root nodes and in the instance variables of strongly reachable objects are strong references. Because the SoftReference object shown in Figure 9-4 is referenced by a strong reference, the SoftReference object is strongly reachable. Assuming that this SoftReference object contains the only reference to the Cow object, the Cow object is softly reachable. The reason the Cow is softly reachable is that the garbage collector can only reach the Cow object from the root nodes by traversing a soft reference.
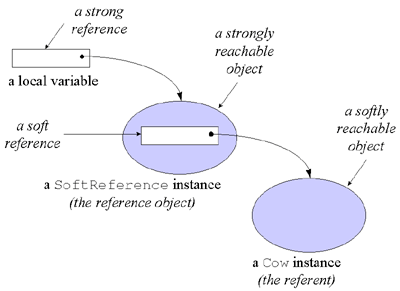
Once a reference object is created, it will continue to hold its soft, weak or phantom reference to its referent until it is cleared by the program or the garbage collector. To clear a reference object, the program or garbage collector need only invoke clear(), a method defined in classReference, on the reference object. Clearing a reference object invalidates the soft, weak, or phantom reference contained in the reference object. For example, if the program or garbage collector were to invoke clear() on the SoftReference object shown in Figure 9-4, the soft reference to the Cow object would be invalidated, and the Cow object would no longer be softly reachable.
|
Sponsored Links
|